A cannon of mass 1500 kg fires a 10-kg shell with a velocity of 200 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. Find the recoil velocity of the cannon across the level ground
a. 1.15 m/s
c. 2.41 m/s
b. 0.94 m/s
d. 1.94 m/s
A
You might also like to view...
How many moons does earth have
A) none B) one C) two D) three E) four
The half-life of 18N is 0.62 s. What is the decay constant for this isotope?
a. 0.43 s–1 b. 1.1 s–1 c. 1.7 × 10^–11 Ci d. The decay constant is not defined for a half-life of less than one second.
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines
A. the half-life of the nucleus. B. the atomic mass. C. the density of the nucleus. D. the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
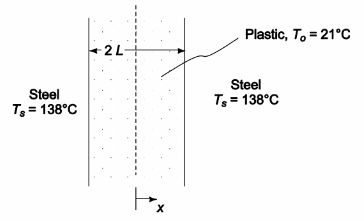
A 2.5-cm-thick sheet of plastic initially at 21°C is placed between two heated steel plates that are maintained at 138°C. The plastic is to be heated just long enough for its midplane temperature to reach 132°C. If the thermal conductivity of the plastic is 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K), the thermal diffusivity is 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s, and the thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible, calculate: (a) the required heating time, (b the temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued, and (c) the time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel plate.
GIVEN
• A sheet of plastic is placed between two heated steel plates
• Sheet thickness (2L) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Initial temperature (To) = 21°C
• Temperature of steel plates (Ts) = 138°C
• Heat until mid-plane temperature of sheet (Tc) = 132°C
• The thermal conductivity of the plastic (k) = 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K)
• The thermal diffusivity (?) = 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s
• The thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible
FIND
(a) The required heating time (b) The temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued (c) The time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel.
ASSUMPTIONS
• The initial temperature of the sheet is uniform
• The temperature of the steel plates is constant
• The thermal conductivity of the sheet is constant
SKETCH