Refer to the graph below. Assume that the economy is initially at full-employment equilibrium at point A. If there is cost-push inflation in this economy and the government pursues an expansionary fiscal policy, then in the long run the:
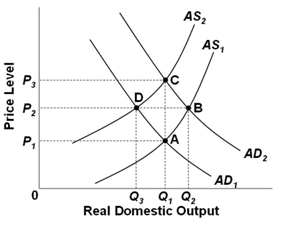
A. Price level will rise from P1 to P2 and real output will be Q2
B. Price level will rise from P1 to P3 and real output will be Q1
C. Price level will rise from P1 to P2 and real output will be Q3
D. Price level will be P1 and real output will be Q1
B. Price level will rise from P1 to P3 and real output will be Q1
You might also like to view...
The damage function method
a. is a behavioral linkage approach to measuring environmental benefits b. uses a technical relationship between an environmental resource and a user of that resource to estimate benefits c. uses the same technique as the contingent valuation approach d. is capable of measuring all aspects of incremental benefits simultaneously
Modern portfolio analysis assumes that individuals
A) are risk-averse. B) attempt to maximize liquidity. C) attempt to maximize returns regardless of risk. D) never take risks.
To grow and prosper, less-developed countries must not:
a. invest in human capital. b. build a strong infrastructure. c. shift resources out of the production of consumer goods and into the production of capital goods. d. shift resources out of the production of capital goods and into the production of consumer goods e. improve the quality of the water supply
If the government regulates a monopoly's price below the socially efficient level, then:
A. deadweight loss decreases and there is a surplus of output. B. deadweight loss increases and there is a surplus output. C. deadweight loss increases and there is a shortage of output. D. deadweight loss decreases and there is a shortage of output.