Snell's Law: A narrow light beam in vacuum contains light of two wavelengths, 480 nm and 700 nm. It strikes a flat piece of glass at an angle of incidence of 60.000°. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.4830 at 480 nm and 1.4760 at 700 nm. Determine the angle between the two wavelengths as the light travels in the glass.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
0.196°
You might also like to view...
A specimen is made of 80 atom % iron and 20 atom % Ni. When sufficient FCC nickel is added to BCC iron, it is possible to produce FCC iron-nickel alloys, which are austenitic. The results of an x-ray diffractometer scan of this specimen with cobalt K? radiation that has a wavelength of 0.1790 nm results in peak intensities at the following angles: 26.1°, 30.56°, 45.99°, 57.49°, and 61.74°.
(a) Is this iron-nickel alloy BCC or FCC? (b) Determine the lattice parameter using the 26.1? peak.
The ____________ of a planet is the region around the planet where the magnetic field is able to deflect the solar wind and other charged particles
a. aurora b. magnetosphere c. hydrosphere d. corona e. Schwarzschild radius
Potential of Point-Charges: Four charged particles (two having a charge +Q and two having a charge -Q) are arranged in the xy-plane, as shown in the figure. These particles are all equidistant from the origin. The electric potential (relative to infinity) at point P on the z-axis due to these particles, is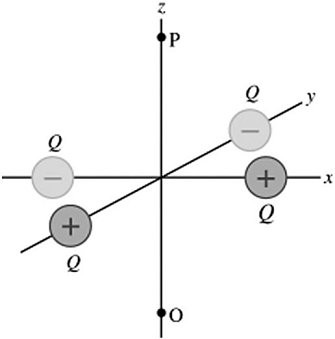
A. zero. B. positive. C. negative. D. impossible to determine based on the information given.
The presence of a Mercurian magnetic field surprised the planetary scientists on the Mariner 10 team because
A) Mercury is low in iron. B) Mercury spins too rapidly to produce a stable dynamo. C) it's still too hot for its core to have differentiated. D) the dynamo theory predicted that Mercury was spinning too slowly for one. E) Mercury lacks an iron core.