If higher inflation ensues from a temporary negative supply shock, and in response, the central bank raises interest rates, then the resulting decrease in AD will return inflation back to its original level ________
A) and no further action will be required by the central bank
B) but the ensuing positive output gap will lead to higher inflation once again so further interest rate increases will be required by the central bank to return inflation back to its long run level
C) but the ensuing negative output gap will lead to short-run increases in AS and the central bank will have to "undo" its original interest rate hike in order to return inflation back to its target rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
C
You might also like to view...
List three characteristics of demand curves. Make sure to explain the shape of the curve and the meaning of the vertical and horizontal intercepts
What will be an ideal response?
The old lyric "the best things in life are free"
a. is not true for any goods. b. is even true for some goods that have a price. c. refers to goods provided by nature or the government. d. refers to goods provided by the market.
A Lorenz curve that becomes less bowed out implies:
A. no change in income distribution. B. a change in income distribution toward more equality. C. an increase in poverty. D. a change in income distribution toward more inequality.
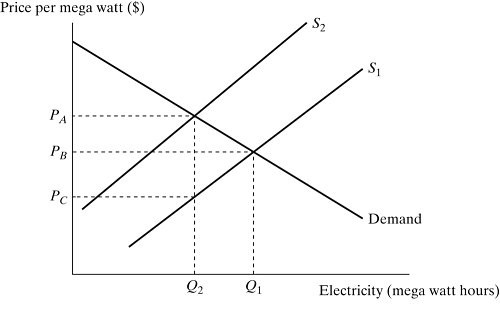
 Figure 9.9 depicts a market for electricity. S1 is the supply curve without the external costs. S2 is the supply curve with the $T tax. Assume electricity production incurs external costs. If the government imposes a pollution tax of $T per mega watt:
Figure 9.9 depicts a market for electricity. S1 is the supply curve without the external costs. S2 is the supply curve with the $T tax. Assume electricity production incurs external costs. If the government imposes a pollution tax of $T per mega watt:
A. the supply curve will shift to the right. B. the supply curve will shift to the left. C. demand curve will shift to the right. D. demand curve will shift to the left.