In Figure 29.1, the area that represents the producer surplus under perfect competition is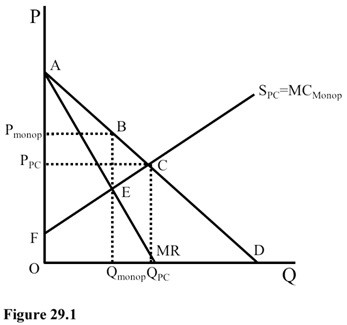
A. FPPCC.
B. PPCAC.
C. FPmonopolyBE.
D. PmonopolyAB.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Specialization and exchange develop under conditions of
A) massive ignorance. B) a total conflict of interests. C) coercion and exploitation. D) none of the above.
Refer to Table 4-1. The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Curly, Moe, and Larry, are willing to pay for a bottle of champagne. If the price of one of the bottles is $24 dollars,
A) Curly will buy two bottles, Moe will buy one bottle and Larry will buy no bottles. B) Curly and Moe receive a total of $80 of consumer surplus from buying one bottle each. Larry will buy no bottles. C) Curly will receive $26 of consumer surplus from buying one bottle. D) Larry will receive $15 of consumer surplus since he will buy no bottles.
You are given the following market data for apples
Demand is represented by: P = 12 - 0.01Q Supply is represented by: P = 0.02Q where P= price per bushel, and Q=quantity. a. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity. b. Suppose the government guaranteed producers a price of $10 per bushel. What would be the effect on quantity supplied? Provide a numerical value. c. By how much would the $10 price change the quantity of apples demanded? Provide a numerical value. d. Would there be a shortage or surplus of apples? e. What is the size of this shortage or surplus? Provide a numerical value.
A _____ is when no one outcome can defeat all others by majority rule
a. cyclical majority b. single-peaked preference c. political business cycle d. political institution