Exhibit 2-19 Production possibilities curves
In Exhibit 2-19, the production possibilities curves for a country are shown for the years Year X and Year Y. Suppose this country was located at point A in Year X and would like to get to point B in Year Y. Construct a plan this country to activate in Year X to achieve this growth.
A. Eliminate unemployment, improve production technology, and acquire additional resources.
B. Produce more consumption goods, eliminate unemployment, and reduce inefficiency.
C. Reduce inefficiency, shift energy sources, and hold technology fixed.
D. It is impossible for this country to achieve point B in Year Y.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Cartels are typically subject to cheating by their members because
A) if the other firms stick to the agreement, a firm can increase its profits by cutting its price. B) barriers to entry do not exist so new entrants will join. C) the U.S. Justice Department will punish any cartel agreement before the cartel has had a chance to operate. D) product differentiation allows the firms in the cartel to cheat.
Refer to Table 2.3. Assume that 2010 is the base year. Real GDP in 2007 is
A) $490.00. B) $568.00. C) $580.00. D) $671.00.
Slick Shades has a constant marginal cost of production equal to $40 and the distributors have a constant marginal cost of distribution equal to $20. If Slick Shades vertically integrates with the perfectly competitive distributors, the relevant demand curve for the combined firm is the ________ demand curve and the combined firm's marginal cost is equal to ________.
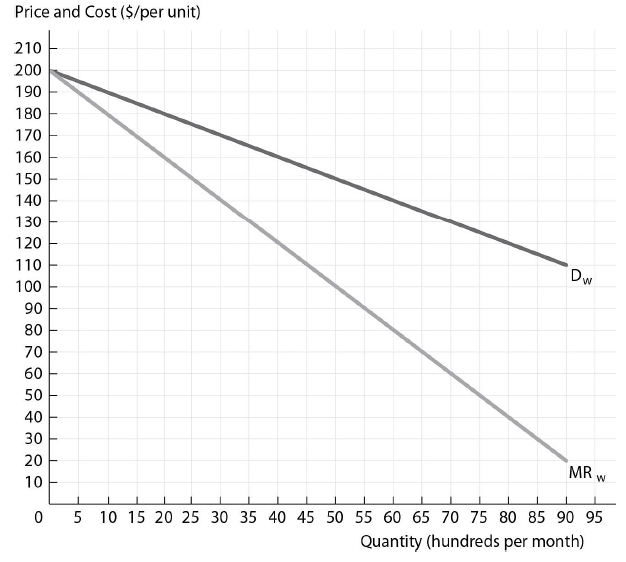
The figure above shows the wholesale demand and marginal revenue curves for Slick Shades Sunglasses, a sunglasses firm with market power. Slick Shades Sunglasses has a constant marginal cost of production and it sells to perfectly competitive independent retail distributors that have a constant marginal cost of distribution.
A) wholesale; $60
B) retail; $40
C) retail; $60
D) wholesale; $40
Transfer prices
a. are an accounting devise to allocate the costs and revenues of intermediate products across divisions b. increase the 'profits' of the profit center producing the intermediate product when they rise c. decrease the 'profits' of the profit center using the intermediate product when they rise d. all of the above