Figure 4-21
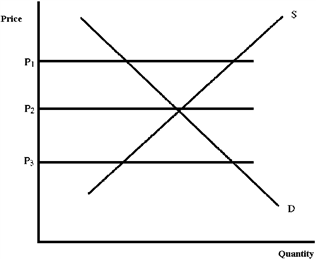
A shortage will tend to occur at which price in Figure 4-21?
a.
P1
b.
P2
c.
P3
c
You might also like to view...
For a Nash equilibrium to be possible, all players must ________
A) be able to predict their outcomes associated with all possible actions of the other players B) have a way to communicate with the other players C) have a strategy which allows for collusion D) Both A and B
Those costs implied by alternatives given up are
a. explicit costs. b. historical costs. c. outlay costs. d. implicit or opportunity costs.
Suppose a perfectly competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium when market demand suddenly decreases. What happens to the industry in the long run?
a. It experiences no change from the original equilibrium b. It experiences a higher equilibrium price and produces less output c. It experiences a lower equilibrium price and produces less output d. It experiences the same equilibrium price but produces more output e. It experiences the same equilibrium price but produces less output
Prospect theory in behavioral economics predicts that as the price of flour increases, bakeries will try to avoid turning off their buyers by:
A. Increasing the unit prices of their products B. Reducing the unit sizes of their products C. Producing more units of their products D. Passively accepting lower profits