If social returns to the production of a good are less than private returns, then we can conclude that relative to the social optimum, the good will be
A) overproduced and underpriced.
B) underproduced and overpriced.
C) overproduced and overpriced.
D) underproduced and underpriced.
A
You might also like to view...
Economists sometimes use the term "countercyclical"
What will be an ideal response?What will be an ideal response?
Suppose scientists provide evidence that people who drink energy drinks are more likely to have a heart attack than people who do not drink energy drinks. We would expect to see
a. no change in the demand for energy drinks. b. a decrease in the demand for energy drinks. c. an increase in the demand for energy drinks. d. a decrease in the supply of energy drinks.
An oligopolist charges a lower price than the short-run profit-maximizing price. How does this affect the firm’s productive efficiency?
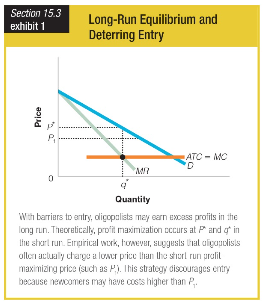
a. The firm fails at productive efficiency because P 1 exceeds the minimum ATC.
b. The firm fails at productive efficiency because P 1 is less than the minimum ATC.
c. The firm achieves productive efficiency because P 1 exceeds MC.
d. The firm achieves productive efficiency because P 1 is less than MC.
In the short run, a profit-maximizing monopolistically competitive firm sets it price:
A. equal to marginal revenue. B. equal to marginal cost. C. above marginal cost. D. below marginal cost.