Calculate the radius in nanometers of the Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom's electron with n = 6
1.91 nm
You might also like to view...
What is the very first step of the scientific method? a. Design an experiment. b. Form a hypothesis
c. Analyze results. d. Generate a conclusion. e. Perform an experiment.
Normal matter is baryonic
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
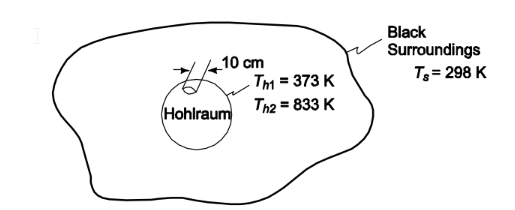
For an ideal radiator (hohlraum) with a 10-cm-diameter opening, located in black surroundings at 16°C, (a) calculate the net radiant heat transfer rate for hohlraum temperatures of 100°C and 560°C, (b) the wavelength at which the emission is a maximum, (c) the monochromatic emission at ?max, and (d) the wavelengths at which the monochromatic emission is 1 per cent of the maximum value.
GIVEN
• An ideal radiator (hohlraum) in black surroundings
• Radiator opening diameter (D) = 10 cm = 0.1 m
• Surrounding temperature (Ts) = 16°C = 289 K
• Hohlraum temperatures
- Th1 = 100°C = 373 K
- Th2 = 560°C = 833 K
FIND
(a) The net radiant heat transfer rate (qr)
(b) The wavelength at which the emission is maximum (?max)
(c) The monochromatic emission at ? max (E?max)
(d) The wavelengths at which the monochromatic emission is 1% E?max
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
The kinetic energy of a pendulum is greatest
a. when its potential energy is greatest. b. at the top of its swing. c. at the bottom of its swing. d. when its total energy is greatest.