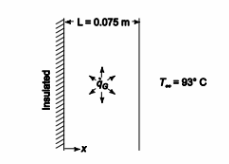
A plane wall, 7.5 cm thick, generates heat internally at the rate of 105 W/m3 . One side of the wall is insulated, and the other side is exposed to an environment at 90°C. The convection heat transfer coefficient between the wall and the environment is 500 W/(m2 K). If the thermal conductivity of the wall is 12 W/(m K), calculate the maximum temperature in the wall.
GIVEN

FIND
- The maximum temperature in the wall (Tmax)
ASSUMPTIONS
- The heat loss through the insulation is negligible
- The system has reached steady state
- One dimensional conduction through the wall
SKETCH
The one dimensional conduction equation, given is
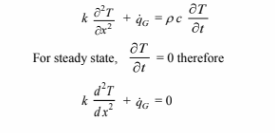
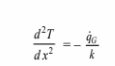
This is subject to the following boundary conditions
No heat loss through the insulation
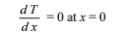
Convection at the other surface
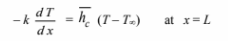
Integrating the conduction equation once
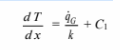
C1 can be evaluated using the first boundary condition
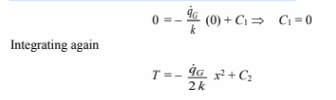
The expression for T and its first derivative can be substituted into the second boundary condition to evaluate the constant C2
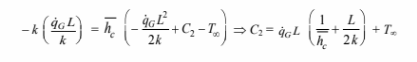
Substituting this into the expression for T yields the temperature distribution in the wall
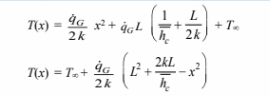
Examination of this expression reveals that the maximum temperature occurs at x = 0
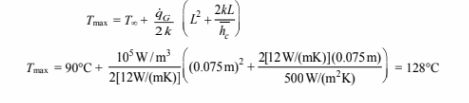
You might also like to view...
Coherent light of a single frequency passes through a double slit with a separation d, to produce a pattern on a screen as distance D from the slits. What would cause the separation between adjacent minima on the screen to increase?
A. increase the index of refraction of the medium in which the setup is immersed B. increase the separation d between the slits C. increase the distance D D. increase the frequency of the incident light
State Kepler's first law of planetary motion
What will be an ideal response?
You are racing away from Earth in a super space ship in which you can continually increase your speed by firing engines that never quit. Which of the following best explains how people on Earth will perceive your speed?
A) They will see your speed getting closer and closer to the speed of light, but never reaching it. B) They will know you are going very fast, but will have no way to know if you ever exceed the speed of light. C) They will see you speed up until you reach the speed of light, and then your speed will remain constant after that. D) They will see you going faster and faster until you reach the speed of light, and after that they won't be able to see you any more.
To create the above spectra, which of the following is NOT true?
![]()
a. A dense gas is excited and the light produced is over all wavelengths.
b. A low-density gas is excited and the light produced is over discrete wavelengths.
c. Light from a low-density gas passes through a warm, dense gas and the light that is produced is at all wavelengths except for a few discrete wavelengths.
d. All of the other choices are not true.