In a free-market economy, prices coordinate society's decisions about
a. how and for whom to produce.
b. what, how, and for whom to produce.
c. how and for whom to produce but not how much to produce.
d. how much and for whom to produce but not how to produce.
b
You might also like to view...
Based on this figure, if the official value of krone is fixed at $0.09 per krone, then the Norwegian krone is ________ and the international reserves of Norway will ________ krone per period. 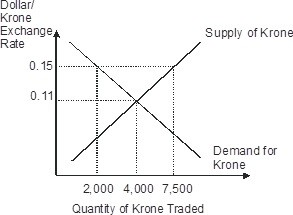
A. overvalued; decrease by 5,500 B. undervalued; increase by 2,000 C. undervalued; increase by 5,500 D. overvalued; decrease by 2,000
The capital account is
A) the reserve assets created by the International Monetary Fund for countries to use in settling international payment obligations. B) the price of one nation's currency in term of the currency of another country. C) a category of the balance of payments transactions that measures flows of real and financial assets. D) a category of the balance of payments transactions that measures the exchange of merchandise, the exchange of services, and unilateral transfers.
When the Fed purchases bonds, the Fed:
A. increases the reserves and the federal funds rate decreases. B. increases the reserves and the federal funds rate increases. C. reduces the reserves and the federal funds rate increases. D. reduces the reserves and the federal funds rate decreases.
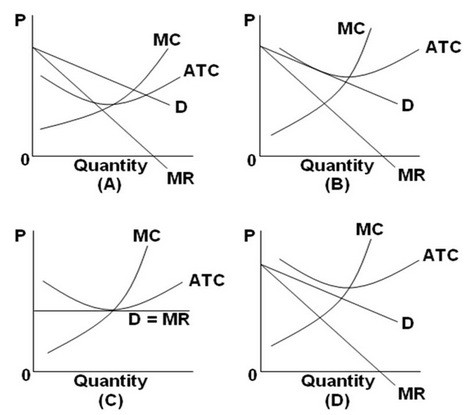 Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce losses for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph:
Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce losses for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph:
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.