Illustrate using a graph how the economy you depicted in (a) will adjust in the long run. On the graph identify the long run price level and the long run level of aggregate output. Explain verbally your results. In your answer make sure you comment on what is happening to wages and prices during this long run adjustment.
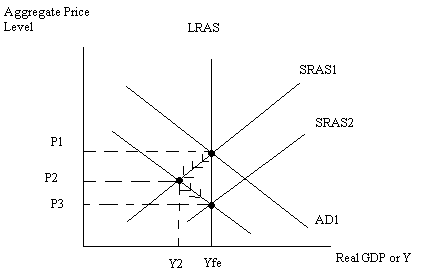
Ans: Over time wages and prices will decrease since the economy is operating at a production level less than Yfe. As nominal wages decrease this will cause the SRAS curve to shift to the right from SRAS1 to SRAS2,Eventually the economy will return to Yfe but with a lower aggregate price level than the initial level. Unemployment will return to the full employment or natural rate of unemployment.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 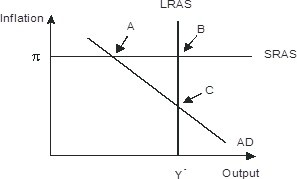
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
If the world real interest rate were to fall below the rate at which domestic saving and investment would be equal ________
A) saving would be greater than investment so the economy would be running a trade deficit B) investment would be greater than saving so the economy would be running a trade deficit C) investment would be greater than saving so the economy would be running a trade surplus D) saving would be greater than investment so the economy would be running a trade surplus E) none of the above
Based on most observations, what are the effects on government budgets from the national health care program?
A) Tax revenues will not flow into the new program immediately. B) The federal government ultimately will have to search for ways to reduce its health care expenditures. C) Federal government expenditures on the program are being phased in immediately. D) the federal government ultimately will lower taxes since the program's cost will decline over time.
Adverse selection in insurance implies that
a. all people face the same risk b. potential customers facing more risk are no more interested in purchasing insurance c. people are not risk averse d. insurers cannot tell the risk levels that different individuals face