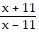A person's weight depends both on the daily rate of energy intake, say C calories per day, and the daily rate of energy consumption, typically between 12 and 20 calories per pound per day. Using an average value of 16 calories per pound per day, a person weighing w pounds uses 16w calories per day. If 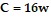 , then weight remains constant, and weight gain or loss occurs according to whether C is greater or less than 16w.To determine how fast a change in weight will occur, a plausible assumption is that dw/dt is proportional to the net excess (or deficit)
, then weight remains constant, and weight gain or loss occurs according to whether C is greater or less than 16w.To determine how fast a change in weight will occur, a plausible assumption is that dw/dt is proportional to the net excess (or deficit) 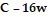 in the number
in the number
of calories per day.Assume C is constant and write a differential equation to express this relationship. Use k to represent the constant of proportionality.
A. 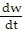 = k(16w - C)
= k(16w - C)
B. 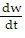 = k(C - 16w)
= k(C - 16w)
C. 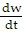 = C(k - 16w)
= C(k - 16w)
D. 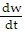 = k(C + 16w)
= k(C + 16w)
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Solve the problem. Round your answer, if appropriate.As the zoom lens in a camera moves in and out, the size of the rectangular image changes. Assume that the current image is 7 cm × 5 cm. Find the rate at which the area of the image is changing (dA/df) if the length of the image is changing at 0.7 cm/s and the width of the image is changing at 0.1 cm/s.
A. 8.4 cm2/sec B. 4.2 cm2/sec C. 5.4 cm2/sec D. 10.8 cm2/sec
Construct a circuit to represent the corresponding symbolic statement.p ? q ? ~r ? (p ? r)
What will be an ideal response?
Translate the sentence into an equation using the variable x. Do not solve the equation. State what the variable represents.The product of 3 and the weight is 799.
A. 3 - x = 799, where x is the weight B. 3 + x = 799, where x is the weight C. 3x = 799, where x is the weight D. 3 = 799x, where x is the weight
Find the quotient and simplify.(x + 11) ÷ 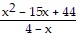
A. - 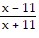
B. -1
C. -(x - 11)(x + 11)
D. -