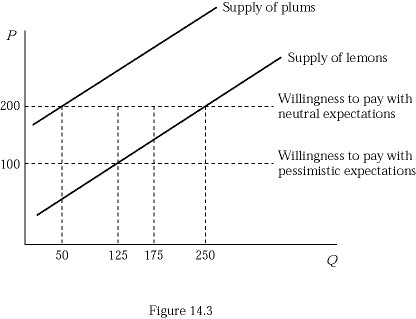
 Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that all of the used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what number of used refrigerators sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that all of the used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), what number of used refrigerators sold will actually be lemons (low quality)?
A. 50
B. 125
C. 175
D. 250
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Larger increases in the demand for labor than in the supply of labor explain:
A. the slowdown in real wage growth. B. skill-biased technological change. C. the substantial increase in real wages. D. increasing wage inequality.
The above figure shows the apartment rental market in Bigtown. If the market is in equilibrium and then the Bigtown Housing Authority imposes a rent ceiling of $500 per apartment, which of the following would occur?
A) a decrease in the search time and expense of finding an apartment B) an increase in the search time and expense of finding an apartment C) an increase in producer surplus but a decrease in consumer surplus D) an increase in efficiency
For a long time, your firm has been paying its workers a wage of $20 per hour and your employees have been happy to work 40 hours per week at this wage
Business is suddenly booming and your firm would really like your workers to agree to a 50-hour work week in order to meet this new demand for your product. You are considering two strategies. Under the first, you would raise the wage for all hours worked from $20 per hour to $22 per hour; under the second, you would leave the wage for the first 40 hours per week at $20 but offer $30 per hour for hours worked above 40 hours (that is, you would offer time and a half for overtime). Both strategies have the same cost of $1,100 if a worker chooses to work 50 hours. Which strategy is more likely to lead your employees to agree to a 50-hour work week?
A monopolist's profit-maximizing price and output correspond to the point on a graph
A) where total costs are the smallest relative to price. B) where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charging the price on the market demand curve for that output. C) where average total cost is minimized. D) where price is as high as possible.