The stiffness of a certain type of steel beam used in building construction has mean 30 kN/mm and standard deviation 2 kN/mm.
a. Is it possible to compute the probability that the stiffness of a randomly chosen beam is greater than 32 kN/mm? If so, compute the probability. If not, explain why not.
b. In a sample of 100 beams, is it possible to compute the probability that the sample mean stiffness of the beams is greater than 30.2 kN/mm? If so, compute the probability. If not, explain why not.
(a) No, we do not know the distribution of the population of beam stiffnesses. In particular, we do not know whether
the population is normal.
(b) Yes, the mean of a large sample is normally distributed, so the Central Limit Theorem can be used.
Let 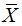 X be the sample mean stiffness. The
X be the sample mean stiffness. The 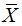 is approximately normally distributed with mean
is approximately normally distributed with mean 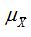 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 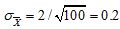 .
.
The z-score of 30.2 is (30.2 ? 30) / 0.2 = 1.00.
The area to the right of z = 1.00 is 1 ? 0.8413 = 0.1587.
You might also like to view...
Grid markers are often used in residential drawings but are not very common in large structures.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Describe three methods for layout of landscape improvements:
What will be an ideal response?
Modern livestock facilities have been designed to make animals as ____ as possible
a. large c. warm b. confined d. comfortable
Testing of an alarm system is being discussed. Technician A says that if the system fails to operate with the relay by-passed. The relay is defective. Technician B says the relay is generally tested with an ammeter. Who is correct?
A. Technician A only B. Technician B only C. Both Technician A and B D. Neither Technician A nor B