The disposable income consumers receive is equal to about what percentage of total income?
A. 70 percent.
B. 95 percent.
C. 30 percent.
D. 50 percent.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
If we compare budget constraint A to budget constraint B in the graph shown, what can be said of the relative prices reflected in the two?
This graph shows three different budget constraints: A, B, and C.
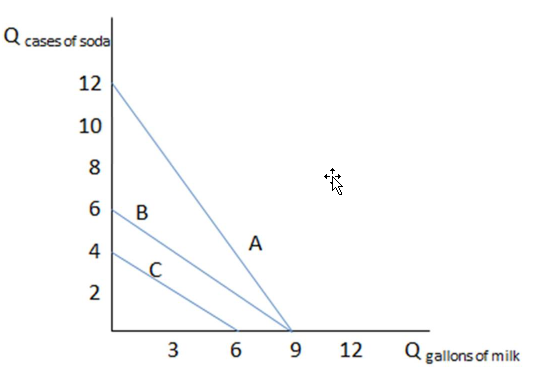
A. Because A is steeper, soda is relatively less expensive in A than in budget constraint B.
B. Because B is steeper, soda is relatively less expensive in A than in budget constraint B.
C. Because B is flatter, soda is relatively more expensive in A than in budget constraint B.
D. Because A is flatter, soda is relatively more expensive in A than in budget constraint B.
Discuss the three principles of equity applied to taxation in the text
If the real exchange rate is greater than 1, then the
a. nominal exchange rate x U.S. price > foreign price. The dollars required to purchase a good in the U.S. would buy more then enough foreign currency to buy the same good overseas. b. nominal exchange rate x U.S. price > foreign price. The dollars required to purchase a good in the U.S. would not buy enough foreign currency to buy the same good overseas. c. nominal exchange rate x U.S. price < foreign price. The dollars required to purchase a good in the U.S. would buy more then enough foreign currency to buy the same good overseas. d. nominal exchange rate x U.S. price < foreign price. The dollars required to purchase a good in the U.S. would not buy enough foreign currency to buy the same good overseas.
According to the text, economists David Gould, G.L. Woodbridge, and Roy Ruffin examined the data on the relationship between increases in imports and the rate of unemployment. They found that
A. free trade leads to increased unemployment. B. there is not a causal link between increases in imports and the rate of unemployment. C. increases in unemployment always precede increases in imports by a period of 6 months to one year. D. increases in imports always precede increases in unemployment by a period of 6 months to one year.