Define the following terms and explain their importance to the study of macroeconomics
a. central bank
b. Federal Open Market Committee
c. supply of money
d. monetary policy
a. A central bank is a government institution that controls the money supply and serves as a banker for commercial banks. The central bank of the United States is the Federal Reserve System, established in 1913.
b. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is made up of the seven governors of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four presidents from the other eleven district banks. The FOMC is responsible for open market operations (and, therefore, the most important component of monetary policy).
c. The supply of money is determined by the Fed and the willingness of banks to make loans. The money supply is influenced by Fed policy that includes open market operations, discount rate changes, and changes in required reserve ratios.
d. Monetary policy is the manipulation of the money supply and interest rates by the Federal Reserve System. The principal objectives of monetary policy are stable prices and economic growth.
You might also like to view...
What is the function of the system of federal regulation created by Congress from 1887 until now?
(a) To change the outcomes of market decisions (b) To enforce the outcomes of market decisions (c) To replace market allocations with economic planning (d) To enforce the law
If MPC = 0.9, equilibrium real GDP is $1,000 . and full-employment real GDP is $2,000 . then how much should government spending change to bring about full employment?
a. +1,000. b. ?100. c. +900. d. +100. e. ?0.9.
Which of the following best illustrates the concept of a store of value?
a. You are a precious-metals dealer, and you are always aware of how many ounces of platinum trade for an ounce of gold. b. You sell items on eBay, and your prices are stated in terms of dollars. c. You keep 6 ounces of gold in your safe-deposit box at the bank for emergencies. d. None of the above is correct.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the long run would be: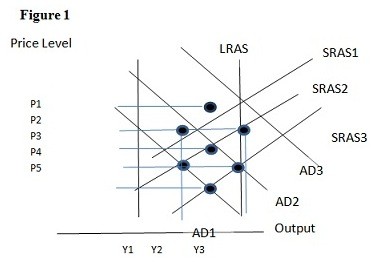
A. P2 and Y2. B. P1 and Y2. C. P4 and Y2. D. P1 and Y1.