Objects A and B, of mass M and 2M respectively, are each pushed a distance d straight up an inclined plane by a force F parallel to the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between each mass and the plane has the same value ?k. At the highest point,
a. KA > KB.
b. KA = KB.
c. KA < KB.
d. The work done by F on A is greater than the work done by F on B.
e. The work done by F on A is less than the work done by F on B.
a
You might also like to view...
Correctly position these four planets within the accretion disk of our early Solar System based on the materials that were present where they formed.
What will be an ideal response?
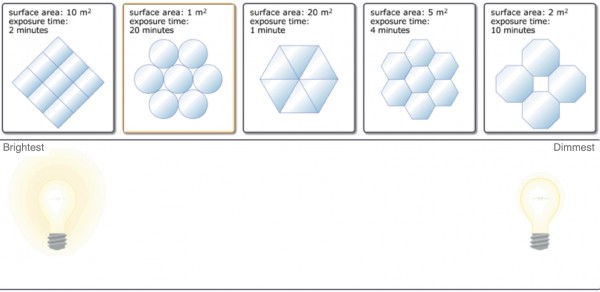
Shown following are the primary mirror arrangements and total light-collecting area of five different telescopes. Notice that although the arrangements look similar to those in Part B, the light-collecting areas are not the same. Also listed is an amount of time (exposure time) that each telescope will be pointed at the same distant galaxy. Again assume that the quality of these mirrors, the detectors, and the observing conditions are identical. Rank the telescopes from left to right based on the brightness of the image each telescope will take of the galaxy in the time indicated, from brightest to dimmest. To rank two (or more) telescopes as equal, drag one on top of the other(s).
For a scientific hypothesis to be valid, there must be a test for proving it
A) right. B) wrong. C) conclusively one way or the other.
The sum of the forces exerted on a 1000-kg car while it is slowing down from 30 m/s to 15.9 m/s is 9500 N. How far does it travel while slowing down?
A) 34 m B) 31 m C) 37 m D) 41 m