Assume that the user cost of capital (C) is simply
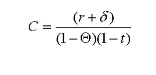
where r is the after tax rate of return, ? is the depreciation rate, ? is the corporate tax rate and,
r is the individual tax rate. Now assume further that the after-tax rate of return is 10 percent
and the economic depreciation rate is 2 percent. The firm faces corporate taxes of 35 percent
with an individual tax rate of 25 percent. What is the user cost of capital in this case?
Solving for C yields C = (0.10 + 0.02)/(1 - 0.35)(1 - 0.25) = 0.2462 or 24.62%.
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 2-8. What is the opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of coconuts in Guatemala?
A) 1/2 of a ton of pineapples B) 1 1/3 tons of pineapples C) 2 tons of pineapples D) 90 tons of pineapples
Suppose the Fed changes the interest rate in an attempt to raise planned investment. But in spite of this, planned investment remains unchanged. The most likely explanation is that
A) we have moved downward along an unchanged rate-of-return line. B) we have moved upward along an unchanged rate-of-return line. C) the rate-of-return line has shifted to the left. D) the rate-of-return line has shifted to the right.
If, as price increases by 10 percent, total revenue decreases by 10 percent demand is
a. elastic. b. unit elastic. c. inelastic. d. perfectly inelastic.
Consider the statement: "When the British government tripled university fees for foreign students in Great Britain, about one-half of them left to study in other countries." This move will ________ university revenues from foreign students in Great Britain.
A. not change B. increase C. decrease D. cannot determine without further information