Which of the following statements about potential GDP is false?
A) The Fed's goal is to have equilibrium GDP close to potential GDP.
B) When GDP is at potential, cyclical unemployment is zero.
C) It occurs when firms are producing at their maximum level of output.
D) It occurs when firms are producing with a workforce of normal size working normal hours.
C
You might also like to view...
Andre, a wheat farmer, is deciding whether or not to add fertilizer to his crops. If he adds 1 pound of fertilizer per acre, the value of the resulting crops rises from $80 to $100 per acre. According to marginal analysis, Andre should add fertilizer if it costs less than
a. $12.50 per pound. b. $20 per pound. c. $80 per pound. d. $100 per pound.
Exhibit 9-7 Two-Firm Payoff Matrix
?
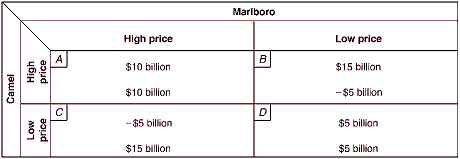
A. Camel charging the high price and Marlboro charging the high price. B. Camel charging the low price and Marlboro charging the low price. C. Camel charging the low price and Marlboro charging the high price. D. Camel charging the high price and Marlboro charging the low price.
Political instability is an impediment to development mainly because it:
A. undermines both domestic and foreign investment in a developing country. B. creates cultural and social differences among groups in developing countries. C. produces excessive levels of domestic saving. D. redistributes income.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1. An under-allocation of resources is occurring in a purely competitive industry whenever the price of the product is greater than marginal cost. 2. In pure competition, resources are optimally allocated when production occurs at the output level where P = MC. 3. Consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a good and the market price of the product. 4. Producer surplus is the difference between the market price a producer receives for a product and the minimum price producers are willing to accept for a product. 5. Competitive markets produce equilibrium prices and quantities that maximize the sum of consumer and producer surpluses.