Suppose that Germany, France, Estonia, and India all have the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Based on the production points in the figure, Germany is most likely to expand its PPF to
A) PPF3 or PPF2.
B) PPF3.
C) PPF1.
D) PPF1. or PPF2.
E) PPF2.
B
You might also like to view...
Classical economists believed that
A) real GDP per person would rise above its subsistence level in the long run. B) real GDP per person would never rise above its subsistence level in the long run. C) the demand for labor increases when the population increases. D) population growth decreases as real GDP per person rises.
Refer to Table 17-5. Oil Can Harry's, a new automobile service shop, is ready to start hiring. The table above shows the relationship between the number of mechanics the firm hires and the quantity of oil changes it produces
a. Suppose the price of an oil change is $20. Complete the table by filling in the values for marginal product and marginal revenue product. b. Oil Can Harry's is an input price-taker. Suppose the wage paid to mechanics is $80 per day. What is the profit-maximizing number of mechanics? c. Suppose the wage rate rises to $100 per day. (i) What happens to the firm's demand curve for mechanics? (ii) What happens to the profit-maximizing quantity of mechanics? d. Suppose the wage rate is $60 per day and the price of an oil change is now $15. (i) What happens to the firm's demand curve for mechanics? (ii) What happens to the profit-maximizing quantity of mechanics?
Refer to the table below. If Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm and the market price $1.00 per unit, what is the profit-maximizing quantity for Sweet Grams to produce at Plant 1?
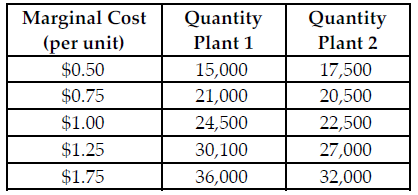
Sweet Grams makes graham cracker snack packages. Sweet Grams is a multi-plant firm with two production facilities. The above table summarizes the total marginal cost of production at various output levels in the separate plants. Assume Sweet Grams is a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 24,500
B) 27,000
C) 32,000
D) 22,500
If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is 0,
a. a price change for one good will be exactly offset by a price change for the other b. neither demand curve would shift following a change in the price of one of the goods c. there is no income effect between the two goods d. the demand for each good is price inelastic e. the demand for each good is price elastic