Mutual recognition of standards refers to
A) the elimination of tariffs and quotas by trading partners.
B) common product safety, environment, labor, and fair competition standards agreed upon by trading partners.
C) the acceptance of a trading partner's standards as valid and sufficient by another trading partner.
D) separate standards held by different trading partners which other partners refuse to recognize.
C
You might also like to view...
The slope of a downward-sloping straight line can be calculated as the distance from the
a. horizontal intercept of the line to the origin divided by the distance from the origin to the vertical intercept of the line. b. origin to the horizontal intercept of the line minus the distance from the origin to the vertical intercept of the line. c. vertical intercept of the line to the origin divided by the distance from the origin to the horizontal intercept of the line. d. vertical intercept of the line to the origin minus the distance from the origin to the horizontal intercept of the line.
Which of the following scenarios shows a benefit of international trade?
a. Edie was able to buy durian from Thailand at a fruit stand in New York City year round. b. The latest film in a superhero series was the top box office draw in the country last week. c. After the knitting factory closed, the building was converted into modern loft apartments. d. Preeti earned about a third of what her U.S. counterpart earned per hour for the same work.
Refer to the graphs shown, which depict a perfectly competitive market and firm. If market demand is D0: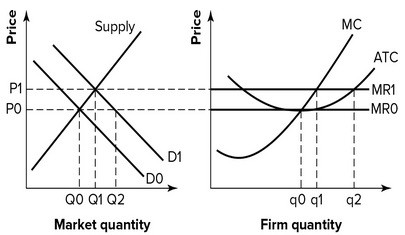
A. the firm will raise the price above P0 to increase profit. B. this market is in short-run equilibrium but not long-run equilibrium. C. this market is in long-run equilibrium because the firm is earning zero economic profit. D. this market is in long-run equilibrium because the firm is earning positive economic profit.
When the federal government takes action to change taxes and spending to stimulate the economy, such policy is:
A. automatic. B. passive. C. discretionary. D. nondiscretionary.