A local flower grower grows products in a plot of land which is exceptionally colorful, and is admired by many passersby. There is no way to charge for this in the price of the flowers. We can safely conclude that
a. the florist produces too many flowers.
b. the florist produces too few flowers.
c. the florist produces the right amount of flowers.
d. society pays the socially optimal amount for the flowers.
b
You might also like to view...
Why is the social marginal benefit of a common property smaller than the value that people, on average, receive from it?
a. Because use of a common property is nonrivalrous. b. Because when one additional person uses the common property, it lowers the value that others receive from it. c. Because entrance fees must be taken into account when determining the social benefit derived from a common property. d. Because "free riders" will use the common property without contributing to its costs.
Use the following graph, where Sd and Dd are the domestic supply and demand for a product and Pc is the world price of that product, to answer the next question.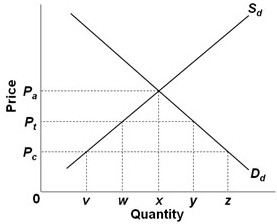 With free trade, that is, assuming no tariff, the outputs produced by domestic and foreign producers respectively would be
With free trade, that is, assuming no tariff, the outputs produced by domestic and foreign producers respectively would be
A. w and y?w. B. w and z?w. C. x and z?x. D. v and z?v.
The price of eggs might go up because:
A) of an increase in the price of bacon. B) the price of chicken feed increased. C) the supply of eggs increased. D) the demand for eggs fell.
How will the exchange rate (foreign currency per dollar) respond to an increase in the relative rate of productivity growth in Canada in the long run?
A) Exchange rates will rise. B) Exchange rates will fall. C) Exchange rates will be unaffected by changes in the relative rate of productivity growth in Canada, both in the short run and in the long run. D) The exchange rate will be affected in the short run, but not in the long run.