If Alan is risk-averse, then he will always
a. choose not to play a game where he has a 50 percent chance of winning $5 and a 50 percent chance of losing $5.
b. choose not to play a game where he has a 75 percent chance of winning $5 and a 25 percent chance of losing $5.
c. choose to play a game where he has a 55 percent chance of winning $5 and a 45 percent chance of losing $5.
d. All of the above are correct.
a
You might also like to view...
Refer to Game Matrix III. The Nash equilibrium is to be found where
Game Matrix III
The following questions refer to the game matrix below. Each firm has a choice of advertising, Ads, or not advertising, No ad. The profits each gets depend upon which it chooses.
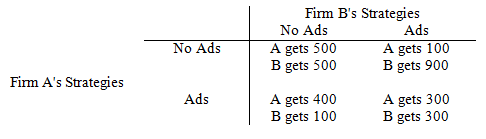
a. neither firm advertises.
b. Firm A advertises, Firm B does not.
c. Firm A does not advertise but Firm B does.
d. both firms choose to advertise.
Cost-reducing technological advancements allow suppliers to earn more profits but have no noticeable effect on the supply curve.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The state is considering adding a satellite campus to its major university. How can marginal analysis assist, even though the university does not attempt to maximize profits?
What will be an ideal response?
Imagine Tom's annual salary as an assistant store manager is $30,000, he owns a building that rents for $10,000 yearly, and his financial assets generate $1,000 per year in interest. One day, after deciding to be his own boss, he quits his job, evicts his tenants, and uses his financial assets to establish a bicycle repair shop. To run the business, he outlays $15,000 in cash to cover all the costs involved with running the business, and earns revenues of $50,000. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Tom has an opportunity cost of $41,000. B. Tom earns an accounting profit of $35,000. C. Tom experiences an economic loss of $6000. D. All of these are true.