Refer to the table below. If the price of A decreases, while the price of B and the consumer's income stay the same, we would expect:
The table below shows the marginal-utility schedules for goods A and B for a hypothetical consumer. The price of good A is $1 and the price of good B is $2. The income of the consumer is $8.
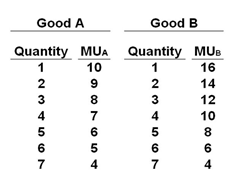
A. MU/P of A to increase, and the consumers will thus buy less of B
B. MU/P of A to increase, and the consumers will thus buy less of A
C. MU/P of A to decrease, and the consumers will thus buy less of B
D. MU/P of A to decrease, and the consumers will thus buy less of A
A. MU/P of A to increase, and the consumers will thus buy less of B
You might also like to view...
The economists discussed in the Application found that states where unemployment benefits ________ grew ________ than in other states
A) increased; slower B) decreased; slower C) increased; faster D) decreased; faster
What is the biggest obstacle to successful economic growth in very low income countries?
a. lack of education b. poor health and limited health care facilities c. high political instability d. lack of technology
Refer to the graphs shown.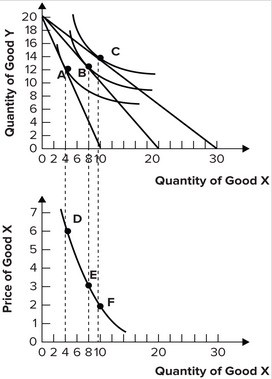 Which of the following combinations of points best illustrates rational consumer choice assuming the consumer's budget is $60, the price of X is $3, and the price of Y is $3?
Which of the following combinations of points best illustrates rational consumer choice assuming the consumer's budget is $60, the price of X is $3, and the price of Y is $3?
A. A and D B. C and F C. B and E D. A and F
Marginal cost
A. Is the change in total cost associated with a one-unit increase in production. B. Is the change in total output from hiring one more factor of production. C. Is the change in the total cost when hiring one more factor of production. D. Falls when there are diminishing returns.