Explain how the shifting spectral lines of spectroscopic binaries let us find their periods
What will be an ideal response?
When aligned in our line of sight, there is no radial velocity, and all lines appear single. A quarter of a period later, one is approaching us with its line blue shifted, and the other is receding. Multiply this time span by four, and the two stars are back in the original positions.
You might also like to view...
What power is produced by a light bulb that yields 12 mW on a 15 cm x 25 cm sheet of paper that is normal to the line directly toward the bulb, if the paper is 1.7 m from the bulb?
A. 2.9 W B. 12 W C. 1.7 W D. 6.6 W
Estimate the heat loss per unit area from a blacktop highway at 110ºC if the air is still and 28ºC.
What will be an ideal response?
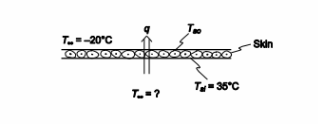
In order to prevent frostbite to skiers on chair lifts, the weather report at most ski areas gives both an air temperature and the wind chill temperature. The air temperature is measured with a thermometer that is not affected by the wind. However, the rate of heat loss from the skier increases with wind velocity, and the wind-chill temperature is the temperature that would result in the same rate of heat loss in still air as occurs at the measured air temperature with the existing wind. Suppose that the inner temperature of a 3-mm-thick layer of skin with a thermal conductivity of 0.35 W/(m K) is 35°C and the ambient air temperature is –20°C. Under calm ambient conditions the heat transfer coefficient at the outer skin surface is about 20 W/(m2 K) but in a 40 mph wind it increases to
75 W/(m2 K). (a) If frostbite can occur when the skin temperature drops to about 10°C, would you advise the skier to wear a face mask? (b) What is the skin temperature drop due to wind?
GIVEN
• Skier’s skin exposed to cold air
• Skin thickness (L) = 3 mm = 0.003 m
• Inner surface temperature of skin (Tsi) = 35°C
• Thermal conductivity of skin (k) = 0.35 W/(m K)
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = –20°C
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Still air (hc0) = 20 W/(m2 K)
? 40 mph air (hc40) = 75 W/(m2 K)
• Frostbite occurs at an outer skin surface temperature (Tso) = 10°C FIND
(a) Will frostbite occur under still or 40 mph wind conditions? (b) Skin temperature drop due to wind chill.
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state conditions prevail
• One dimensional conduction occurs through the skin
• Radiative loss (or gain from sunshine) is negligible
SKETCH
How do we know the total mass of the Milky Way Galaxy that is contained within the Sun's orbital path?
A) by counting the number of stars visible in this region of the galaxy B) by estimating the amount of gas and dust in between the stars C) by using the law of conservation of angular momentum to calculate the orbital speeds of nearby stars D) by applying Newton's version of Kepler's third law to the orbits of the Sun or other nearby stars around the center of the Galaxy