In the diagram:
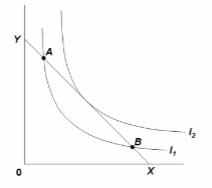
A. the consumer is indifferent between points A and B, but neither point maximizes his utility.
B. the consumer is indifferent between points A and B and either point will maximize his utility.
C. any combination of X and Y entailing more of Y and less of X than shown at B would be
preferred.
D. any combination of X and Y entailing more of X and less of Y than shown at A would be
preferred.
A. the consumer is indifferent between points A and B, but neither point maximizes his utility.
You might also like to view...
Assume a firm purchases resources a and b under purely competitive conditions and combines these resources to produce X. Product X is sold in a purely competitive market. The MPs of a and b are 6 and 3 respectively and the prices of a and b are $12 and
$6 respectively. If equilibrium exists, the price of X will be: A. $1. B. $.50. C. $2. D. $5.
The quantity of good M is measured along the vertical axis, and the quantity of good N is measured along the horizontal axis. If the prices of both goods M and N declines by 50% each, then the budget line
A) shifts inward to the left by 50%. B) shifts outward to the right by 50%. C) shifts outward to the right by 100%. D) rotates clockwise by 180 degrees.
Related to the Economics in Practice on page 26: How did the introduction of the microwave oven in 1960 affect the market for frozen food?
A. It increased the financial cost of alternative methods of food preparation, such as conventional ovens. B. It encouraged people to leave the work force by making cooking easier and less time-consuming. C. It reduced the opportunity cost of eating frozen food by decreasing the amount of time required to prepare frozen meals. D. It made frozen foods more appealing by increasing the variety of meals that could be frozen and reheated.
The largest single transfer program at the federal level is
A. the agricultural support program. B. unemployment compensation. C. farm subsidies. D. Social Security.