A particle (q = 3.0 mC, m = 20 g) has a speed of 20 m/s when it enters a region where the electric field has a constant magnitude of 80 N/C and a direction which is the same as the velocity of the particle. What is the speed of the particle 3.0 s after it enters this region?
A. 68 m/s
B. 44 m/s
C. 56 m/s
D. 80 m/s
E. 36 m/s
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
What are the clouds of Venus mainly composed of?
A. carbon dioxide B. sulfuric acid droplets C. methane D. water vapor
A small sphere attached to a light rigid rod rotates about an axis perpendicular to and fixed to the other end of the rod. Relative to the positive direction of the axis of rotation, the angular positions of the sphere are positive, its angular velocity is positive, and its angular acceleration is negative. The sphere is
A. rotating clockwise and slowing down. B. rotating counterclockwise and slowing down. C. rotating clockwise and speeding up. D. rotating counterclockwise and speeding up. E. first rotating clockwise and then counterclockwise.
Ozone is a pollutant
a. in the stratosphere. b. near ground level. c. in nitric-acid-rich polar stratospheric clouds. d. in chlorine gas near Earth's surface. e. that can be used as fertilizer on farm fields.
A 1.2-kg mass is projected up a rough circular track (radius = 0.80 m) as shown. The speed of the mass at point A is 8.4 m/s, and at point B, it is 5.6 m/s. What is the change in mechanical energy between A and B caused by the force of friction?
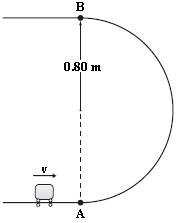
a.
?2.7 J
b.
?8.8 J
c.
?4.7 J
d.
?6.7 J
e.
?19 J