The risk of crowding out is greater the closer the economy is to full employment.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
If the economy were operating at full employment, crowding out would be inevitable. At full employment, we would be on the production possibilities curve, using all available resources. Therefore, additional government purchases can occur only if private sector purchases are reduced. In real terms, crowding out implies less private sector output. If the economy is in recession, it is possible to get more public sector output (like highways, schools, or defense) without cutbacks in private sector output.
You might also like to view...
The self-correcting tendency of the economy means that falling inflation eventually eliminates:
A. exogenous spending. B. recessionary gaps. C. expansionary gaps. D. unemployment.
Which of the following would a Keynesian economist be most likely to stress?
a. Supply creates its own demand. b. Businesses will not produce goods and services if they do not think people will buy them. c. You cannot spend your way out of a recession. d. When the unemployment rate is high, wage rates will fall. e. A dollar saved is a dollar earned; a high rate of saving is the key to prosperity.
Which of the following factors best explains why consumers might prefer to go to a restaurant that was similar to another restaurant in terms of décor and food choices but had fewer customers?
a. the presence of network externalities b. the idea that some people receive utility from goods they believe are popular c. income and substitution effects d. switching costs
Refer to the data provided in Table 9.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.
Table 9.1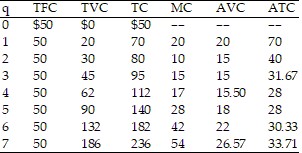 Refer to Table 9.1. If the market price is $17, then in the long run the firm will
Refer to Table 9.1. If the market price is $17, then in the long run the firm will
A. operate and expand. B. operate but not expand. C. shut down, but not go out of business. D. go out of business.