The amount of a good that must be given up to produce another good is the concept of:
A. scarcity.
B. specialization.
C. opportunity cost.
D. efficiency.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If Sam wants to increase her total revenue from her sales of flowers and she knows that the demand for flowers is price elastic, she should
A) lower her price to increase the demand and shift the demand curve rightward. B) raise her price because she knows that the quantity demanded will also increase. C) raise her price because she knows that the percentage decrease in the quantity demanded will be smaller than the percentage increase in price. D) lower her price because she knows that the percentage increase in the quantity demanded will be greater than the percentage decrease in price.
Briefly describe the following tasks of macroeconomists: forecasting; analysis; research; and data development
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to Table 5.4. If outcomes 1 and 2 are equally likely at Job A, then in absolute value
A) W = X = $10. B) W = X = $20. C) W = Y = $100. D) W = Y = $200. E) W = Y = $300.
Table 10.1 shows the cash flows and discounted cash flows for three mutually exclusive projects available to a company. Assume an interest rate of 5%. Which project should the company choose if they want to recover their initial investment as soon as possible?
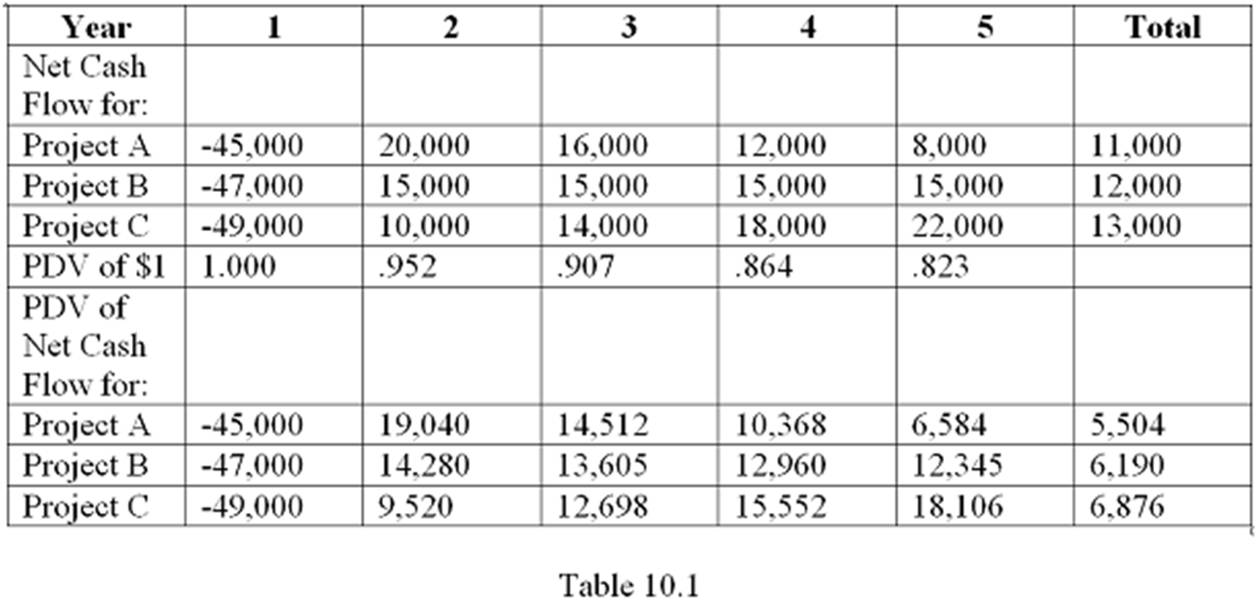
A. Project A
B. Project B
C. Project C
D. It cannot be determined from the information given.