Quantitative easing refers to a policy action in which a central bank
A. decreases interest rates directly without altering bank reserves.
B. sells government securities to directly decrease bank reserves.
C. buys government securities to directly increase bank reserves.
D. increases interest rates directly without altering bank reserves.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
With respect to Figure 3.1, the classicists argued that
a. the relevant aggregate supply curve is labeled B. b. the curves labeled B and G are both relevant during recessions. c. only the supply curve labeled M is important. d. None of the above
According to the matrix shown, the outcome of the "game" will be:
This prisoner's dilemma game shows the payoffs associated with two firms, A and B, in an oligopoly and their choices to either collude with one another or not.
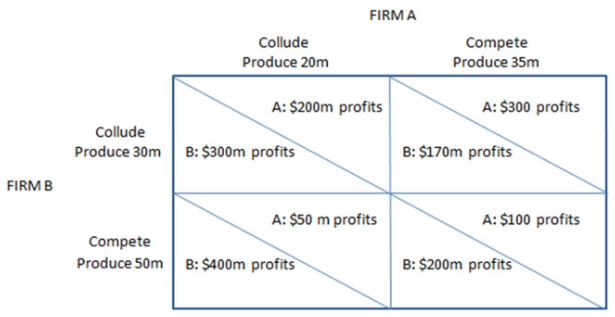
A. both firms will collude and act like a joint monopolist.
B. both firms will compete.
C. Firm A will compete and Firm B will collude.
D. Firm B will compete and Firm A will collude.
One of the largest foreign portfolio investments in the U.S. comes from:
A. Chinese purchases of U.S. capital goods. B. U.S. purchases of Chinese government debt. C. U.S. purchases of Chinese consumption goods. D. Chinese purchases of U.S. government debt.
Recall the Application about the best speed at which to sail an ocean cargo ship to answer the following question(s).Weighing the benefits and costs of the different speeds at which to sail an ocean cargo ship addresses the economic concept known as:
A. the principle of opportunity cost. B. the marginal principle. C. the principle of voluntary exchange. D. the principle of diminishing returns.