According to the ________ theory of regulation, regulators must take into account the preferences of legislators, consumers, and producers.
A. share-the-gains, share-the-pains
B. public interest
C. capture
D. general interest
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 4-8. What is the value of producer surplus after the imposition of the ceiling?
A) $40,000 B) $100,000 C) $300,000 D) $430,000
Dorothy lives in a city with high air pollution. Pollution is a bad, but she is able to avoid air pollution by wearing a face mask. Her preferences are given by
U(q1,q2 ) = (q1 - P)2q22 where q1 is the amount of time she spends wearing a mask, P is the amount of pollution and q2 is a composite of other goods (p2 = 1 ). Dorothy must decide how much to wear a mask and how much q2 to purchase. The price of masks is pM. Assume q1* > P when answering this question. a. Derive Dorothy's demand for masks, q1*(p1,Y, P) b. How does the quantity of pollution affect the demand for masks? That is, find q1*/P. c. How does her income influence the quantity of masks she purchases? That is, find q1*/Y. d. What condition must hold for the assumption q1* > P to hold?
According to the information in the table shown, if someone were earning $20,000 in Mexico, approximately what would he need to earn in the United States to enjoy the same amount of goods and services?
This table shows the price-level adjustment as compared to the United States.
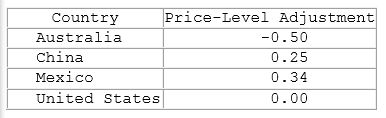
A. $30,303
B. $35,000
C. $20,030
D. $15,000
When workers earn below-subsistence wages in a free market economy, some workers will starve. As a result, the supply of labor curve will shift:
A. rightward, causing the wage to rise. B. leftward, causing the wage to fall further. C. leftward, causing the wage to rise. D. rightward, causing the wage to fall further.