Explain the meaning of the term dead capital, and discuss why its existence retards economic growth
What will be an ideal response?
Dead capital means a capital resource without a clearly defined owner. Although dead capital is often used in production the lack of clearly defined title of ownership typically leads to inefficient use of the resource. The inefficient use of dead capital reduces the rate of return on investments and thus the incentive to increase investment in capital goods are reduced. Lower levels of capital investment diminish the rate of economic growth.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. Suppose all firms in this industry have identical costs to this firm and are producing 15 units of output. One can predict thatQuantityTotal RevenueExplicit CostsImplicit Costs1050365157563620100937251251258301501619
A. firms will attempt to lower their implicit costs. B. price must rise. C. new firms will enter the industry. D. old firms will exit the industry.
Use the following production possibilities frontiers to answer the next question.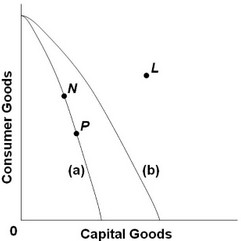 Curve (a) is the initial frontier for the economy, and the nation is initially producing combination P. A shift from curve (a) to curve (b) suggests that the economy can then increase its production of capital goods
Curve (a) is the initial frontier for the economy, and the nation is initially producing combination P. A shift from curve (a) to curve (b) suggests that the economy can then increase its production of capital goods
A. so as to produce the combination L. B. and consumer goods simultaneously, except at the point where the curve intersects the vertical axis. C. but will have to hold constant its production of consumer goods. D. only if it reduces its production of consumer goods.
In a competitive market, if the production process involves an external benefit, the market will
a. produce the economically efficient outcome. b. result in a market price that is higher than the efficient one. c. result in a market price that is lower than the efficient one. d. result in too much of the good being produced compared to the ideal efficient outcome.
Other things the same, a decrease in the U.S. interest rate
a. induces firms to invest more. b. shifts money demand to the left. c. makes the U.S. dollar appreciate. d. increases the opportunity cost of holding dollars.