A 0.0040-kg lead bullet is traveling at a speed of 220 m/s when it embeds in a block of ice at 0°C. If all the heat generated goes into melting ice, what quantity of ice is melted? (Lf = 80 kcal/kg, the specific heat of lead = 0.03 kcal/kg/°C, and 1 kcal = 4 186 J)
a. 1.6E–2 kg
b. 5.8E–4 kg
c. 4.6E–3 kg
d. 2.9E–4 kg
e. 1.9E–5 kg
d
You might also like to view...
Which of the following materials would you expect to have the lowest Young’s modulus?
(a) Aluminum metals (b) Alumina ceramic (c) Polyvinylchloride (d) Rubber
A 1.500 m long uniform beam of mass 30.00 kg is supported by a wire as shown in the figure. The beam makes an angle of 10.00 degrees with the horizontal and the wire makes and angle of 30.00 degrees with the beam. A 50.00 kg mass, m, is attached to the end of the beam. What is the tension in the wire?
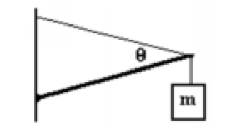
A. 2,034 N
B. 1,855 N
C. 1,435 N
D. 1,255 N
E. 1,035 N
A circular conducting loop lies in the xy plane of a certain reference frame. We are looking down on the loop with the +z axis pointing up at us, what kind of field actually pushes charge carriers around the loop (if current flows in the loop at all)?
A. The changing magnetic field. B. An electric field. C. No current flows in the loop.
Electrons are used to produce X-rays by allowing a beam of electrons to strike a heavy metal surface. What is true about the wavelengths of the bremsstrahlung X-rays that are produced in such a situation?
A. There are a few specific wavelengths that are produced for a given metal and their wavelength is independent of the energy of the electron beam used. B. There is a single wavelength of X-ray produced that depends on the energy of the electron beam used. C. There is a continuous range of wavelengths produced, down to a minimum that depends on the energy of the electron beam used. D. There is a continuous range of wavelengths produced, up to a maximum that depends on the energy of the electron beam used.