Some anti-cancer drugs block signal transduction pathways activated by growth factors. Which of the following would be a good target for such a drug?
A. An inhibitor of a protein kinase cascade.
B. An inhibitor of Ca2+ release
C. An inhibitor of adenylyl cyclase.
D. An inhibitor of phospholipase C.
E. A phosphatase inhibitor.
A. An inhibitor of a protein kinase cascade.
You might also like to view...
F. F. Blackman performed experiments to investigate the effects of various factors on photosynthesis. In one of his experiments, Blackman found that if light intensity was low, photosynthesis could be accelerated by increasing the amount of light, but not by increasing the temperature or carbon dioxide concentration. What can you conclude from this specific experiment?
A. Light is important for photosynthesis B. Carbon dioxide is important for photosynthesis C. High temperatures are important for photosynthesis D. Photosynthesis generates oxygen Clarify Question What is the key concept addressed by the question? What type of thinking is required? Gather Content What do you already know about photosynthesis? What other information is related to the question? Choose Answer Do you have all the information needed to draw a supported conclusion? Reflect on Process Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
Which one of the following sets of homopolymeric peptides is generated in vitro with the synthetic RNA polymer consisting of the repeating trinucleotide (GUC)n?
A. Poly(Val), Poly(Ala), and Poly(Leu) B. Poly(Ser), Poly(Gly), and Poly(Arg) C. Poly(Arg), Poly(Ser), and Poly(Val) D. Poly(Val), Poly(His), and Poly(Asn)
Evidence suggests that the ________ evolved from an ancient prokaryote whose plasma membrane was infolded
a. endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope b. mitochondrion c. ribosome d. chloroplast
What molecular complex is shown in the illustration?
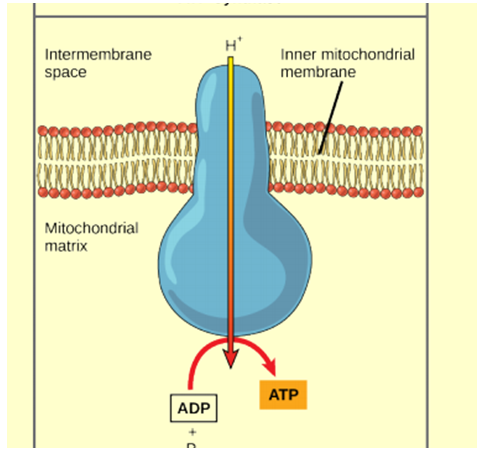
a. Complex II
b. Ubiquinone
c. ATP synthase
d. NADH