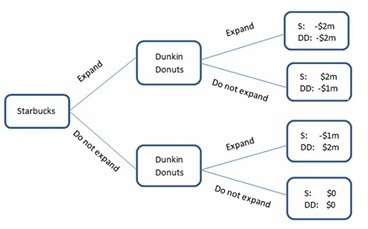
 This figure displays the choices being made by two coffee shops: Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to expand in an area. The area can handle only one of them expanding, and whoever expands will cause the other to lose some business. If they both expand, the market will be saturated, and neither company will do well. The payoffs are the additional profits (or losses) they will earn.According to the figure shown, Dunkin Donuts:
This figure displays the choices being made by two coffee shops: Starbucks and Dunkin Donuts. Both companies are trying to decide whether or not to expand in an area. The area can handle only one of them expanding, and whoever expands will cause the other to lose some business. If they both expand, the market will be saturated, and neither company will do well. The payoffs are the additional profits (or losses) they will earn.According to the figure shown, Dunkin Donuts:
A. does not have a dominant strategy.
B. should not expand, regardless of what Starbucks chooses to do.
C. has first-mover advantage.
D. should expand, regardless of what Starbucks chooses to do.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Crest Toothpaste offers new whitening toothpaste one year, a new gel swirl design the next year, and an improved cleaning formula the year after. Crest Toothpaste does this because it is
A) a monopoly trying to decrease its costs. B) a perfectly competitive firm trying to increase its price. C) a monopolistically competitive firm trying to maintain its economic profit. D) driving its competitors out of business. E) a perfectly competitive firm trying to increase its costs so it can increase its price.
Suppose a taxpayer has an income of $50,000 and a taxable income of $45,000, and pays $5,000 in taxes. If the taxpayer talks of being taxed at a 10 percent tax rate, she is referring to the
A. Nominal tax rate. B. Average tax rate. C. Marginal tax rate. D. Effective tax rate.
Earth Movers & Shakers operates 3 iron ore mines. The accompanying table shows each mine's total daily production and the current number of miners at each mine. All miners work for the same wage, and each miner in any given mine produces the same number of tons per day as every other miner in that mine. Total Tons Per DayNumber of MinersMother Lode10025Scraping Bottom3010Middle Drift7515 The opportunity cost of moving one miner from Mother Lode to another mine is:
A. 3 tons per day. B. 4 tons per day. C. 1 ton per day. D. 2 tons per day.
If the demand curve for product B shifts to the right as the price of product A declines, then:
A. both A and B are inferior goods. B. A is a superior good and B is an inferior good. C. A is an inferior good and B is a superior good. D. A and B are complementary goods.