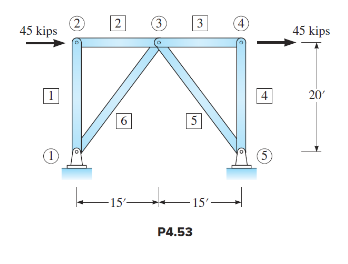
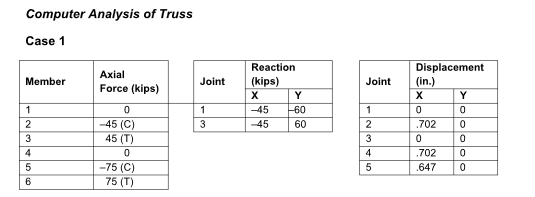
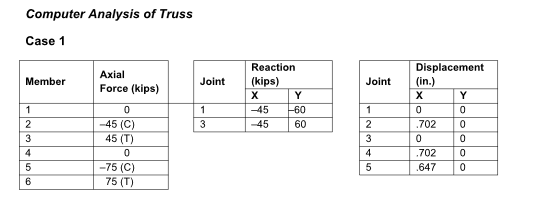
Computer analysis of a truss. The purpose of this study is to show that the magnitude of the joint displacements as well as the magnitude of the forces in members may control the proportions of structural members. For example, building codes typically specify maximum permitted displacements to ensure that excessive cracking of attached construction, such as exterior walls and windows, does not occur (Photo 1.1 in Section 1.3). A preliminary design of the truss in Figure P4.53 produces the following bar areas: members 1 through 4, 5 in. 2 , and members 5 and 6, 2 in. 2 . Also E = 29,000 kips/in. 2 . Case 1: Determine all bar forces, joint reactions, and joint displacements, assuming pin joints. Use the computer program to plot the deflected shape. Case 2: If the maximum horizontal
displacement of joint 4 is not to exceed 0.25 in., determine the minimum required area of the diagonal truss bars, members 5 and 6. For this case assume that the diagaonal members have the same areas, while all other truss members have cross-sectional area of 5 in. 2 . Round the area to the nearest whole number. Photo 1.1: Wind damage. Shortly after thermopane windows were installed in this high-rise office building, they began failing and falling out, scattering broken glass on passers-by beneath. Before the building could be occupied, the structural frame had to be stiffened and all the original glass panels had to be replaced by thicker, tempered glass—costly procedures that delayed the opening of the building for several years.

Case 2
From the computer analysis, the horizontal deflection at Joint 4 is 0.702 in. if the area of the
diagonal truss members is set equal to 2 in. 2 . To limit the deflection to 0.25 in, the minimum
required area is 6.7 in. 2 . Rounding to the nearest whole number makes the required area 7
in. 2
You might also like to view...
When a cylinder head bolt torque specification requires that the fastener is first torqued, then turned through a further set number of degrees, the method is known as:
A. template torque B. twist torque C. constant clamping force D. bolt tensioning
Explain the action of fluid trapped in a sealed system.
What will be an ideal response?
What is the difference between a type S corporation and a limited liability company?
What will be an ideal response?
Which part of an analog flue gas instrument may alter readings because of voltage and current issues?
A) The selector switch B) The batteries C) The circuit board D) The pump