Refer to the graph below, showing the long-run supply and demand curves in a purely competitive market. The curves suggest that in this industry, the marginal benefit to consumers of each unit of the product is:
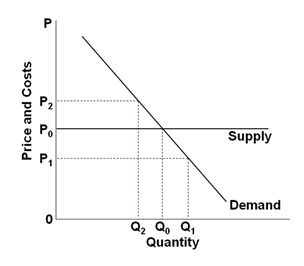
A. Constant
B. Increasing
C. Decreasing
D. Not indicated in the graph
C. Decreasing
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is an example of a barter transaction?
A) An individual pays her electric bill with a check. B) An individual pays her electric bill with currency. C) An individual provides three light bulbs to her neighbor in exchange for two gallons of milk. D) An individual deposits three twenty-dollar bills in her checking account.
The hidden-cost fallacy occurs when
a. A firm considers irrelevant costs b. A firm ignores relevant costs c. A firm considers overhead or depreciation costs to make short-run decisions d. Both a and c
Although monopolistically competitive markets offer consumers a wide variety of differentiated products, there may still be insufficient variety if
a. there are large fixed costs in the market. b. there are no barriers to entry in the market. c. the business-stealing externality is present in the market. d. the government does not impose regulations on the market.
Edward Chamberlin argued that brand names
a. hampered market efficiency. b. were instrumental in enhancing market efficiency. c. were useful in enhancing market efficiency when the government enforced the use of exclusive trademarks. d. were likely to be more socially efficient when used in conjunction with advertising.