When consumers face rising gasoline prices, they typically
a. reduce their quantity demanded more in the long run than in the short run.
b. reduce their quantity demanded more in the short run than in the long run.
c. do not reduce their quantity demanded in the short run or the long run.
d. increase their quantity demanded in the short run but reduce their quantity demanded in the long run.
a
You might also like to view...
The value of a model is determined by
A) the usefulness of its predictions in the real world. B) the extent of the profit earned by applying it. C) the realism of its assumptions. D) the model's attention to real world details.
A firm is experiencing theft problems at its warehouse. A consultant to the firm believes that the dollar loss from theft each week (T) depends on the number of security guards (G) and on the unemployment rate in the county where the warehouse is located (U measured as a percent). In order to test this hypothesis, the consultant estimated the regression equation T = a + bG + cU and obtained the following results: 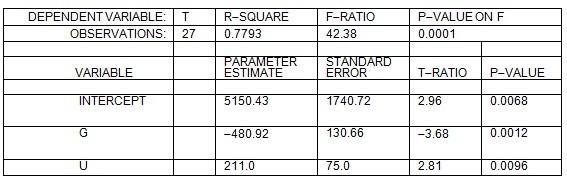 Based on the above information, if the firm hires 6 guards and the unemployment rate in the county is 10% (U = 10), what is the predicted dollar loss to theft per week?
Based on the above information, if the firm hires 6 guards and the unemployment rate in the county is 10% (U = 10), what is the predicted dollar loss to theft per week?
A. $8,300 per week B. $5,150 per week C. $9,955 per week D. $4,375 per week
Economic profits are maximized at the point at which
A. accounting profits are equal to zero. B. marginal revenues equal marginal costs. C. accounting profit exceeds economic profit. D. total revenues are greater than total costs.
Suppose there are two firms on a river and the production processes of both require clean water. The upstream firm's process dirties the water, which it dumps back into the river. The downstream firm must clean the water before using it in its production process. If the two firms would merge
A. the internal costs of the downstream firm become external costs of the merged firm. B. the external costs of the merged firm would equal the external costs of the upstream firm, which would then be passed on to its customers. C. the external costs of the upstream firm are private costs after the merger. D. the total costs of production fall since the external costs disappear.