A mercury bath at 60°C is to be heated by immersing cylindrical electric heating rods, each 20 cm tall and 2 cm in diameter. Calculate the maximum electric power rating of a typical rod if its maximum surface temperature is 140°C.
GIVEN
• Cylindrical heating rods in a mercury bath
• Mercury temperature (T?) = 60°C
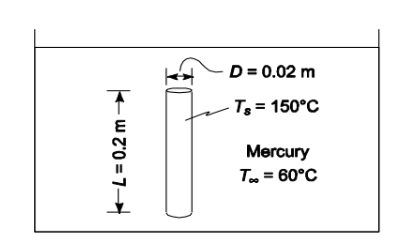
• Rod diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m
• Rod height (L) = 20 cm = 0.2 m
• Maximum surface temperature (Ts) = 140°C
FIND
• The maximum electric power rating ( q e) of a rod
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• The rods are in a vertical position
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for mercury at the mean temperature of 100°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 10.51 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 0.093 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.0162 Also Density at 50°C (?50) = 13,506 kg/m3
Density at 15°C (?150) = 13,264 kg/m3 To find the thermal expansion coefficient (?),
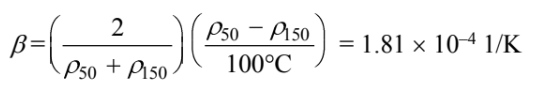
The Grashof number at the top of the cylinder is
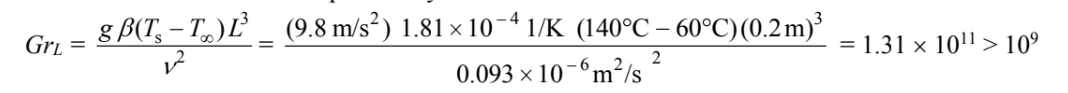
Therefore, the boundary layer is turbulent and the average heat transfer coefficient is

The maximum electric power rating of a rod is equal to the maximum rate of heat transfer from a rod
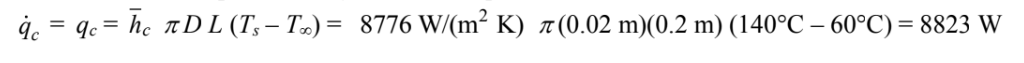
You might also like to view...
What basic type of reaction is illustrated by the general equation A + B ? AB?
a. Combination b. Decomposition c. Double-replacement d. Single-replacement
Mercury orbits the sun about once every 80 days. Mercury is observed to keep the same side facing the sun at all times. If Mercury had oceans, how much time would elapse between its high tides
A. there would be no tides B. 40 days C. 80 days D. 160 days
A barge with vertical sides is 10.0 m wide and 60.0 m long and is floating in fresh water. How much deeper into the water does the barge sink when 300,000 kg of coal are loaded on the barge?
A) 25.0 cm B) 50.0 cm C) 75.0 cm D) 1.00 m E) 1.50 m
You walk 53 m to the north, then you turn 60° to your right and walk another 45m Determine the direction of your displacement vector. Express your answer as an angle relative to east
A) 57° N of E B) 50° N of E C) 69° N of E D) 63° N of E