What is a wave period?
A) The horizontal distance between two successive crests or troughs
B) The number of waves passing a fixed point per second
C) The time for a wave to move the distance of one wavelength
D) The end of a wave train
C
You might also like to view...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the cap-and-trade approach?
What will be an ideal response?
Students in introductory science courses commonly are taught that the scientific method consists of formulating a hypothesis, testing that hypothesis, and developing a theory based on the results of the test(s)
In practice, the scientific method is much more complex. Explain how. What will be an ideal response?
The type of fault shown in this figure is a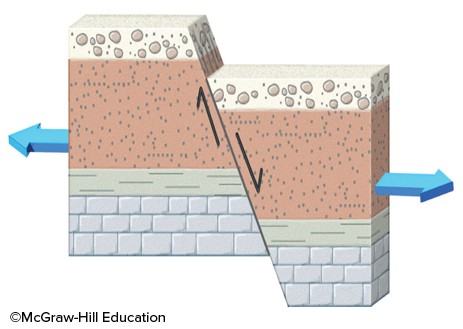
A. thrust fault. B. strike-slip fault. C. reverse fault. D. normal fault.
Explain how the properties of conformality and equivalence always pose a dilemma to the mapmaker
What will be an ideal response?