Goods produced in the United States and sold in other countries are called
A) imports.
B) foreign goods.
C) capital goods.
D) exports.
E) capital account goods.
Ans: D) exports.
You might also like to view...
The following graph applies to a consumer for whom good x is an inferior good. The price of x falls from p to p', and one of the curves below represents the consumer's (uncompensated) demand curve while the other represents the consumer's compensated demand (or MWTP) curve.
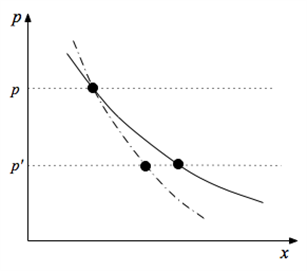
c. Once the consumer has optimized at the new price p', illustrate the new (uncompensated) demand and the new MWTP curve. d. For curves that have shifted, explain why; for curves that have not shifted, explain why as well. What will be an ideal response?
The main avenue by which a temporary change in government purchases in the classical model affects the labor supply is by
A) changing the population. B) affecting the value of the stock market. C) increasing business confidence. D) affecting workers' wealth.
In the RBC model, supply shocks
A) are always favorable by definition, but come at irregular intervals. B) are always adverse by definition, but come at irregular intervals. C) alternate between favorable and adverse shocks. D) follow demand shocks with the opposite effect on output.
We say that equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market is allocatively efficient because
a. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is maximized b. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is minimized c. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is zero d. consumer surplus is maximized e. producer surplus is zero