Discuss the observational phenomena that are associated with the existence of neutron stars
What will be an ideal response?
If a neutron star is tilted in the right direction, from Earth it is seen as a pulsar. A pulsar appears as a rapidly flashing source of radio, and possibly optical, radiation. The flashes or pulses occur several times a second and are precisely timed. They are caused by the spin of the pulsar, as radiation is beamed out along its magnetic poles. The spin rate decreases very slowly with time as the pulsar loses energy. Also, Hubble Space Telescope recently found a very hot, tiny faint object close to the Sun, too small and hot to be a white dwarf.
You might also like to view...
When light illuminates a grating with 7000 lines per centimeter, its second order maximum is at 62.4°. What is the wavelength of the light?
A) 336 nm B) 363 nm C) 452 nm D) 633 nm E) 752 nm
A small bulb is rated at 7.5 W when operated at 125 V. Its resistance (in ohms) is
a. 0.45. b. 7.5. c. 17. d. 940. e. 2 100.
Density: Substance A has a density of 3 g/cm3 and substance B has a density of 4 g/cm3. In order to obtain equal masses of these two substances, what must be the ratio of the volume of A to the volume of B?
A. 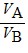 =
= 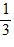
B. 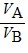 =
= 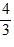
C. 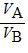 =
= 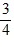
D. 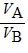 =
= 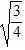
E. 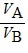 =
= 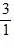
Two charged particles held close to each other are released. As they move, the force on each particle increases. Therefore, the particles
a. Opposite signs. b. The same sign. c. Charges cannot be determined.