A nonbinding price ceiling (i) causes a surplus. (ii) causes a shortage. (iii) is set at a price above the equilibrium price. (iv) is set at a price below the equilibrium price
a. (i) only
b. (iii) only
c. (i) and (iii) only
d. (ii) and (iv) only
b
You might also like to view...
Imagine Tom's annual salary as an assistant store manager is $30,000, he owns a building that rents for $10,000 yearly, and his financial assets generate $1,000 per year in interest. One day, after deciding to be his own boss, he quits his job, evicts his tenants, and uses his financial assets to establish a bicycle repair shop. To run the business, he outlays $15,000 in cash to cover all the costs involved with running the business, and earns revenues of $50,000. What are Tom's economic profits?
A. $35,000 B. $50,000 C. $24,000 D. $6,000
Marginal product of labor is:
a. the extra output produced by an additional worker, all else unchanged. b. the extra wage earned by an additional worker, all else unchanged. c. the total output produced when an extra worker is hired. d. the total revenue earned when an extra worker is hired.
The following table provides nominal exchange rates for the U.S. dollar.CountryForeign currency/dollarDollar/foreign currencySwitzerland (franc)1.7300.578Brazil (real)1.8210.549 Based on these data, the nominal exchange rate equals approximately ________ reals per Swiss franc or, equivalently, ________ Swiss francs per real.
A. 0.950; 1.053 B. 1.053; 0.950 C. 3.551; 0.282 D. 0.282; 3.551
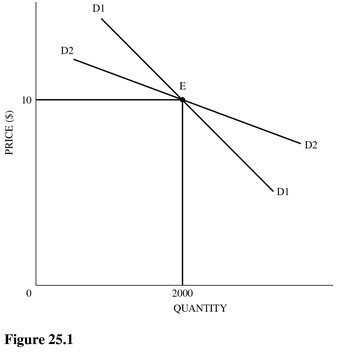 Refer to Figure 25.1 for an oligopoly firm. Assume that the existing price and quantity are $10 and 2,000 units. Which of the following statements is most likely correct?
Refer to Figure 25.1 for an oligopoly firm. Assume that the existing price and quantity are $10 and 2,000 units. Which of the following statements is most likely correct?
A. Demand curves D1 and D2 both assume that rivals will not match any price changes. B. Demand curve D1 assumes that rivals match any price changes. C. Demand curves D1 and D2 both assume that rivals match any price changes. D. Demand curve D2 assumes that rivals match any price changes.