Figure 3-15
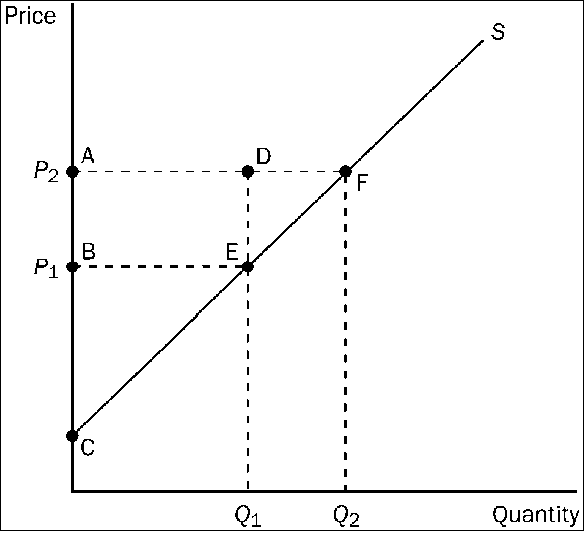
Refer to . Which area represents producer surplus when the price is P1?
a.
BCE
b.
ACF
c.
ABED
d.
DEF
a
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large increase in government purchases will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. expansionary; higher; potential B. recessionary; higher; potential C. recessionary; lower; lower D. expansionary; higher; higher
Suppose that a firm can invest $100 today in a project and receive $105 a year from today. There is no inflation, and the annual interest rate in the economy is 4%. The firm should
A) invest in the project because the opportunity cost is the same as the return on the investment. B) invest in the project because the opportunity cost is greater than the return on the investment. C) invest in the project because the opportunity cost is less than the return on the investment. D) not invest in the project because the opportunity cost is less than the return on the investment.
On a graph we draw indifference curves to illustrate Steven's preferences for steak and broccoli. If two of Steven's indifference curves cross, then it cannot be the case that Steven
a. regards steak and broccoli as complements. b. spends more of his income on steak than on broccoli. c. likes steak and likes broccoli. d. always prefers more steak to less steak and more broccoli to less broccoli.
Which of the following statements is TRUE of external costs?
A. There are no good ways to correct for external costs. B. When external costs exist, the price of the good will be deceptively low leading to an overallocation of resources. C. External costs should only be corrected for if the correction will not increase the market price. D. External costs should not be corrected since people will bear the costs whether they are corrected or not.