Using the figure below, identify the labeled part.
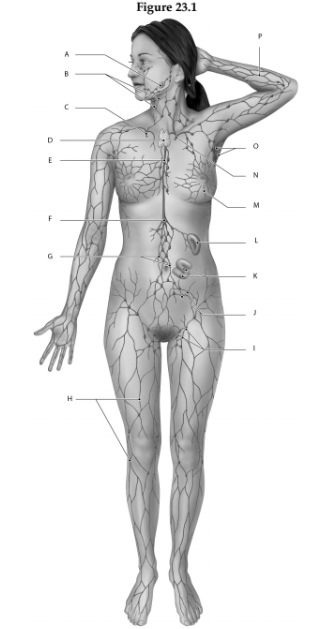
1. Label A: ______________________________
2. Label B: ______________________________
3. Label C: ______________________________
4. Label D: ______________________________
5. Label E: ______________________________
6. Label F: ______________________________
7. Label G: ______________________________
8. Label H: ______________________________
9. Label I: ______________________________
10. Label J: ______________________________
11. Label K: ______________________________
12. Label L: ______________________________
13. Label M: ______________________________
14. Label N: ______________________________
15. Label O: ______________________________
16. Label P: ______________________________
1. Tonsil
2. Cervical lymph nodes
3. Right lymphatic duct
4. Thymus
5. Thoracic duct
6. Cisterna chyli
7. Lumbar lymph nodes
8. lymphatics of lower limb
9. Inguinal lymph nodes
10. Pelvic lymph nodes
11. Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
12. Spleen
13. Lymphatics of mammary gland
14. Thoracic (left lymphatic) duct
15. Axillary lymph nodes
16. Lymphatics of upper limb
You might also like to view...
Chloride ions follow the concentration gradient, but require a membrane protein for passage. Which transport method is occurring?
A. Pinocytosis B. Active transport C. Facilitated diffusion D. Diffusion
What hormone(s) is secreted by the corpus luteum?
a. FSH b. estrogen c. progesterone d. LH e. both estrogen and progesterone
________ is another term for the internal nares
A) Glottis B) Pharynx C) Epiglottis D) Choanae
Which of the following statements about control of body movement is FALSE?
A. The corticospinal motor pathways control most fine, discrete muscle activity. B. The brainstem pathways control postural and most other coordinated body movements. C. The cerebellum fine-tunes ongoing movement and helps to coordinate movements. D. The corticobulbar pathways begin in the sensorimotor cortex and end in the brainstem. E. The corticospinal tracts from the right sensorimotor cortex control movements of limbs on the right side of the body.