Derive an equation in the form ch = f(T, D, U?) for flow of air over a long horizontal cylinder for the temperature range 0°C to 100°C, using as a basis.
GIVEN
• Flow over a long horizontal cylinder
• Air temperature range is 0°C < T < 100°C
FIND
• An equation in the form ch = f(T, D, U?) based on Equation (6.3)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Prandtl number variation is negligible
SKETCH
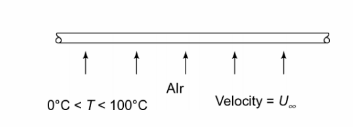
for dry air the Prandtl number is constant (Pr = 0.71) for the given
temperature range. neglecting the variation of Prandtl number term
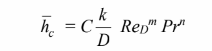
where n = 0.37 for air and C and m are given in
To obtain the desired functional relationship, the kinematic viscosity (?) and thermal conductivity (k)
must be expressed as a function of temperature.
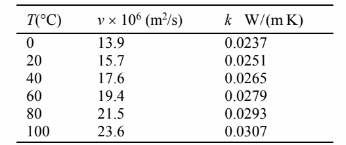
Plotting these data, we see that the relationship is nearly linear in both cases. Therefore, a linear least
squares regression line will be fit to the data
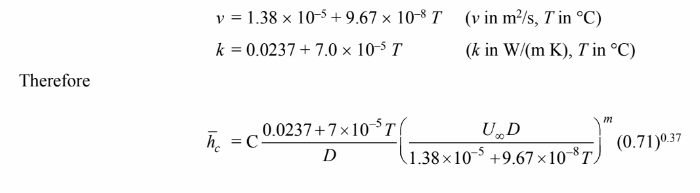

You might also like to view...
During precipitation-hardening, at peak strength the precipitate changes from coherent to _________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
If we place living cells in a nonpolar solvent like methane or ethane,
A) their membranes will thicken, preventing molecular transport across the membrane B) they will rapidly explode due to pressure caused by the solvent building up inside the cell C) their membranes will most likely dissolve as cell membranes are also nonpolar D) they will function in much the same way as they do in water
On a clear day, the sky appears to be more blue toward the zenith (overhead) than it does toward the horizon. This occurs because
A) the atmosphere is denser higher up than it is at the earth's surface. B) the temperature of the upper atmosphere is higher than it is at the earth's surface. C) the sunlight travels over a longer path at the horizon, resulting in more absorption. D) the atmosphere is more reddish over the ocean.
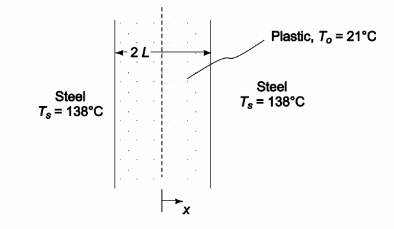
A 2.5-cm-thick sheet of plastic initially at 21°C is placed between two heated steel plates that are maintained at 138°C. The plastic is to be heated just long enough for its midplane temperature to reach 132°C. If the thermal conductivity of the plastic is 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K), the thermal diffusivity is 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s, and the thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible, calculate: (a) the required heating time, (b the temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued, and (c) the time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel plate.
GIVEN
• A sheet of plastic is placed between two heated steel plates
• Sheet thickness (2L) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Initial temperature (To) = 21°C
• Temperature of steel plates (Ts) = 138°C
• Heat until mid-plane temperature of sheet (Tc) = 132°C
• The thermal conductivity of the plastic (k) = 1.1 × 10–3 W/(m K)
• The thermal diffusivity (?) = 2.7 × 10–6 m2/s
• The thermal resistance at the interface between the plates and the plastic is negligible
FIND
(a) The required heating time (b) The temperature at a plane 0.6 cm from the steel plate at the moment the heating is discontinued (c) The time required for the plastic to reach a temperature of 132°C 0.6 cm from the steel.
ASSUMPTIONS
• The initial temperature of the sheet is uniform
• The temperature of the steel plates is constant
• The thermal conductivity of the sheet is constant
SKETCH