The current deficit minus net interest is called the
A. net current deficit.
B. primary deficit.
C. current surplus.
D. primary current deficit.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The Balance of Payments
If there is a change in the federal funds rate from a target rate due to an increase in the demand for reserves, the Fed can maintain the target by:
A) causing an upward movement along the supply of reserves curve. B) causing the supply curve of reserves to shift to the left. C) causing a downward movement along the supply of reserves curve. D) causing the supply curve of reserves to shift to the right.
A beneficial oil-price shock increases labor demand. What happens to current employment and the real wage rate?
A) Both employment and the real wage rate would increase. B) Both employment and the real wage rate would decrease. C) Employment would increase and the real wage would decrease. D) Employment would decrease and the real wage would increase.
Consider an economy that has the following monetary data.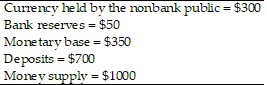 The monetary base and the money supply are expected to grow at a constant rate of 20% per year. Inflation and expected inflation are 20% per year. Suppose that bank reserves and currency pay no interest, all currency is held by the public, and bank deposits pay no interest. What is the cost to the public of the inflation tax?
The monetary base and the money supply are expected to grow at a constant rate of 20% per year. Inflation and expected inflation are 20% per year. Suppose that bank reserves and currency pay no interest, all currency is held by the public, and bank deposits pay no interest. What is the cost to the public of the inflation tax?
A. $190 B. $60 C. $140 D. $200