Refer to Figure 5-5. Suppose the current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output because of an externality. The economically efficient output is Q2. In that case, diagram shows
A) the effect of an excess demand in a market.
B) the effect of a subsidy granted to producers of a good.
C) the effect of a positive externality in the consumption of a good.
D) the effect of a negative externality in the consumption of a good.
C
You might also like to view...
When policy makers attempt to focus on internal balance, they
A) must be talking only about domestic goals. B) must be talking about domestic and international goals. C) must consider both domestic policy and trade. D) Any of the above might be considered internal balance.
If consumers expect that the price of pretzels will decrease next week, what would happen today?
A) Demand today for pretzels would decrease. B) Demand today for pretzels would increase. C) Demand today for pretzels would be unaffected. D) Supply today of pretzels would decrease.
Figure 7.5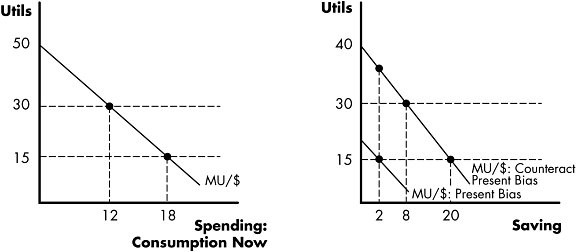 The consumer must decide how to split $20 between spending and saving.Refer to Figure 7.5. If the consumer uses cognition to offset present bias, he/she will maximize utility at a marginal utility per dollar of ________ utils for consumption and ________ utils for saving.
The consumer must decide how to split $20 between spending and saving.Refer to Figure 7.5. If the consumer uses cognition to offset present bias, he/she will maximize utility at a marginal utility per dollar of ________ utils for consumption and ________ utils for saving.
A. 15; 15 B. 15; 30 C. 30; 15 D. 30; 30
A monopolist that chooses price
A) necessarily produces less than a monopolist that chooses quantity, hence the laws against price fixing. B) produces the same amount as a monopolist that chooses quantity. C) produces more than a monopolist that chooses quantity, thus the irony of laws against price fixing. D) could produce more or less than a monopolist that chooses quantity since the demand curve is not specified.