When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis, an increase in the money supply causes the equilibrium value of money
a. and equilibrium quantity of money to increase.
b. and equilibrium quantity of money to decrease.
c. to increase, while the equilibrium quantity of money decreases.
d. to decrease, while the equilibrium quantity of money increases.
d
You might also like to view...
If d is the depreciation rate and K is the capital stock, the amount of investment required to keep the economy in a steady state is given by:
A) I = d - K. B) I = d + K. C) I = d × K. D) I = d/K.
Refer to Figure 4-9. For each unit sold, the price sellers receive after the tax (net of tax) is
A) $12. B) $8. C) $4.40. D) $3.
The tendency to experience losses as more painful than the pleasures that result from gains of the same magnitude is known as:
A. the availability heuristic. B. the present-aim standard of rationality. C. loss aversion. D. regression to the mean.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: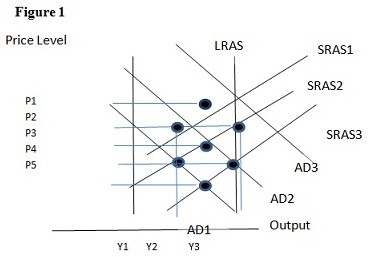
A. P1 and Y2. B. P3 and Y1. C. P2 and Y2. D. P2 and Y3.